UniversalToken

Delivery-vs-payment smart contract description
Objective
The purpose of the contract is to allow secure token transfers/exchanges between 2 stakeholders (called holder1 and holder2). It is used for secondary market assets transfers.
From now on, an operation in the Swaps smart contract (transfer/exchange) is called a trade. Depending on the type of trade, one/multiple token transfers will be executed.
How does it work?
The simplified workflow is the following:
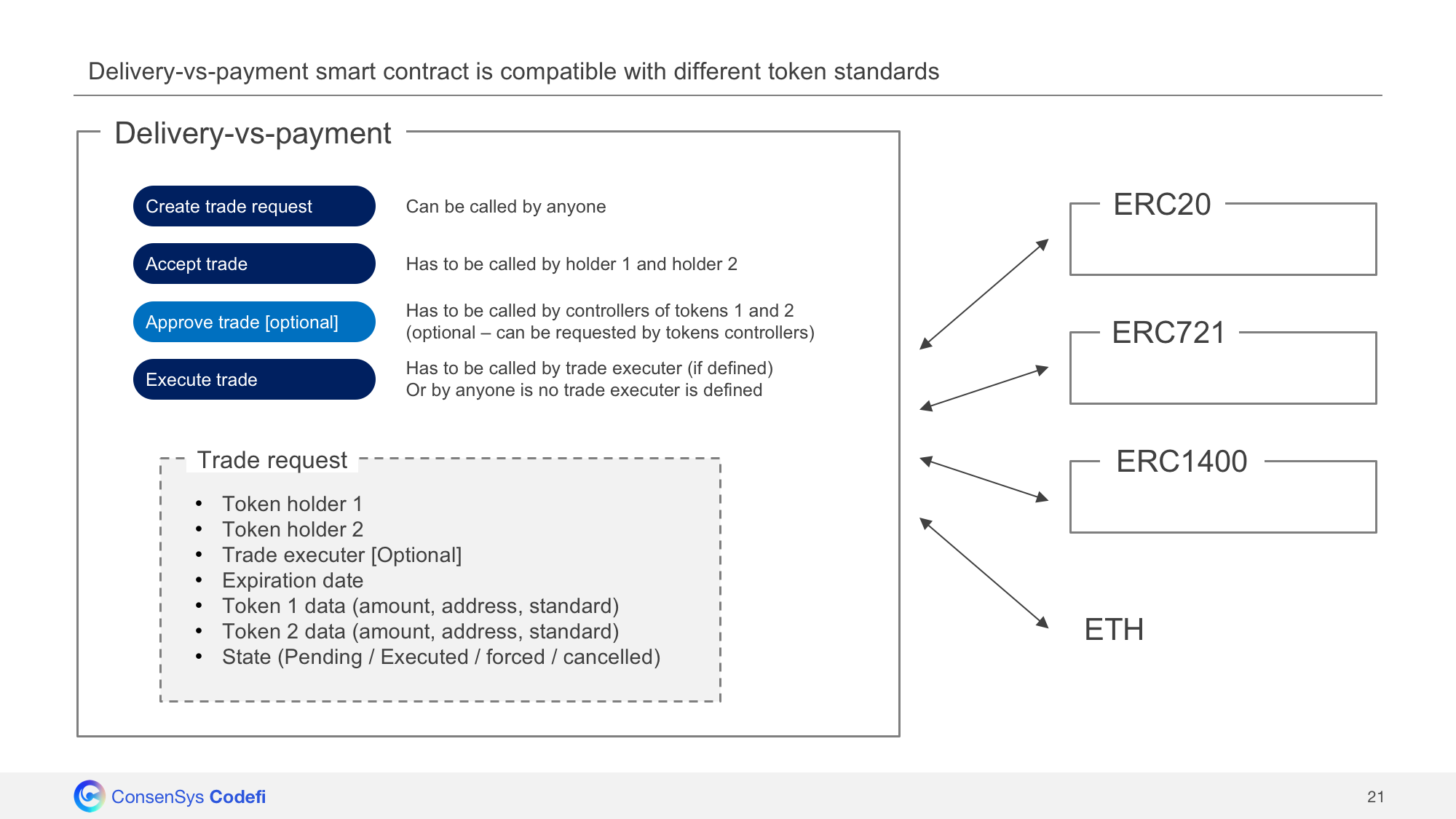
- A trade request is created in the Swaps smart contract, it specifies:
- The token holder(s) involved in the trade - The trade executer (optional) - An expiration date - Details on the first token (address, requested amount, standard) - Details on the second token (address, requested amount, standard) - Whether the tokens need to be escrowed in the Swaps contract or not - The current status of the trade (pending / executed / forced / cancelled) - The trade is accepted by both token holders
- [OPTIONAL] The trade is approved by token controllers (only if requested by tokens controllers)
- The trade is executed (either by the executer in case the executer is specified, or by anyone)
Features
Standard-agnostic
The Swaps smart contract is standard-agnostic, it supports ETH, ERC20, ERC721, ERC1400. The advantage of using an ERC1400 token is to leverages its hook property, thus requiring ONE single transaction (operatorTransferByPartition()) to send tokens to the Swaps smart contract instead of TWO with the ERC20 token standard (approve() + transferFrom()).
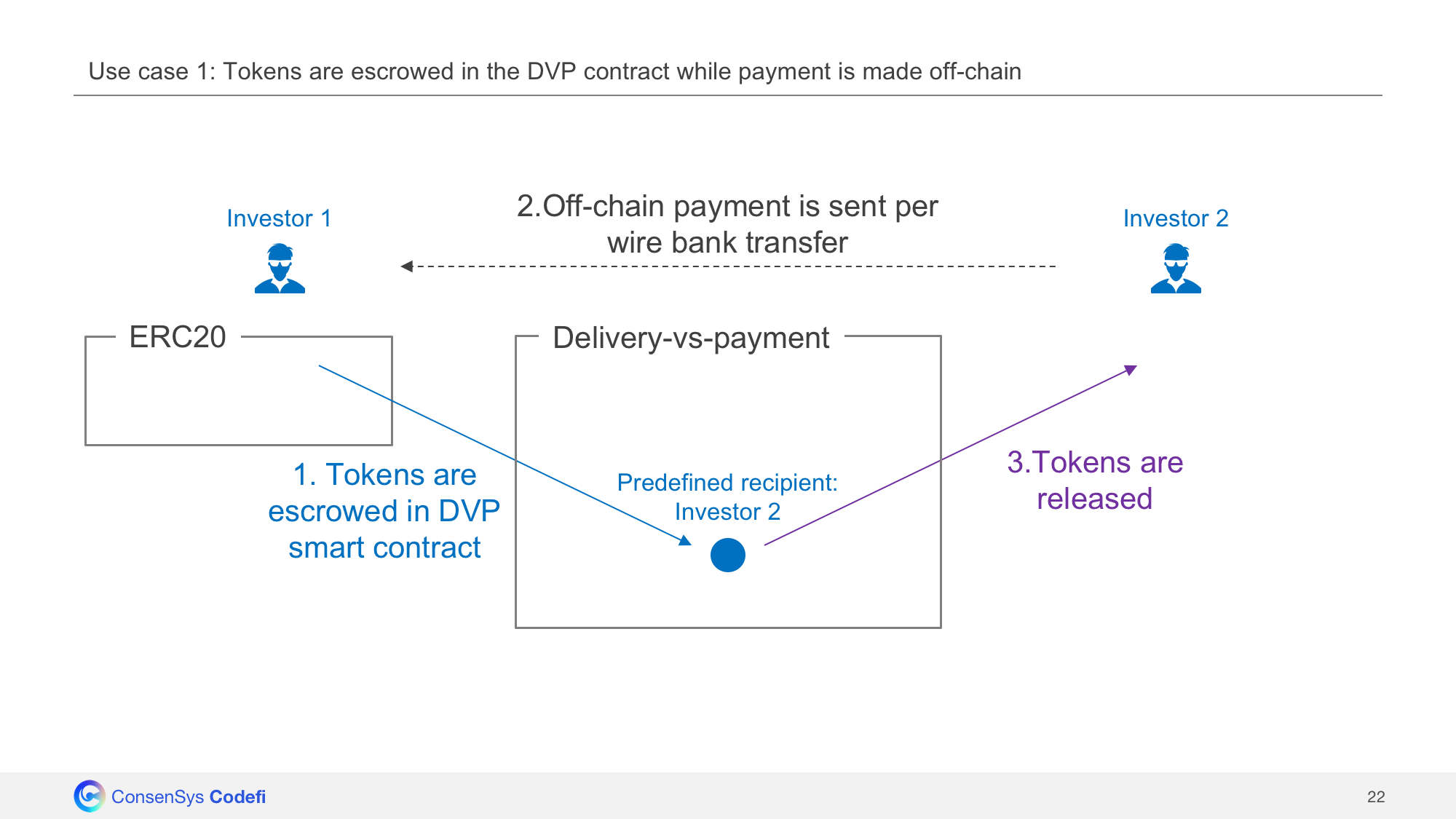
Off-chain payment
The contract can be used as escrow contract while waiting for an off-chain payment. Once payment is received off-chain, the token sender realeases the tokens escrowed in the Swaps contract to deliver them to the recipient.
Escrow vs swap mode
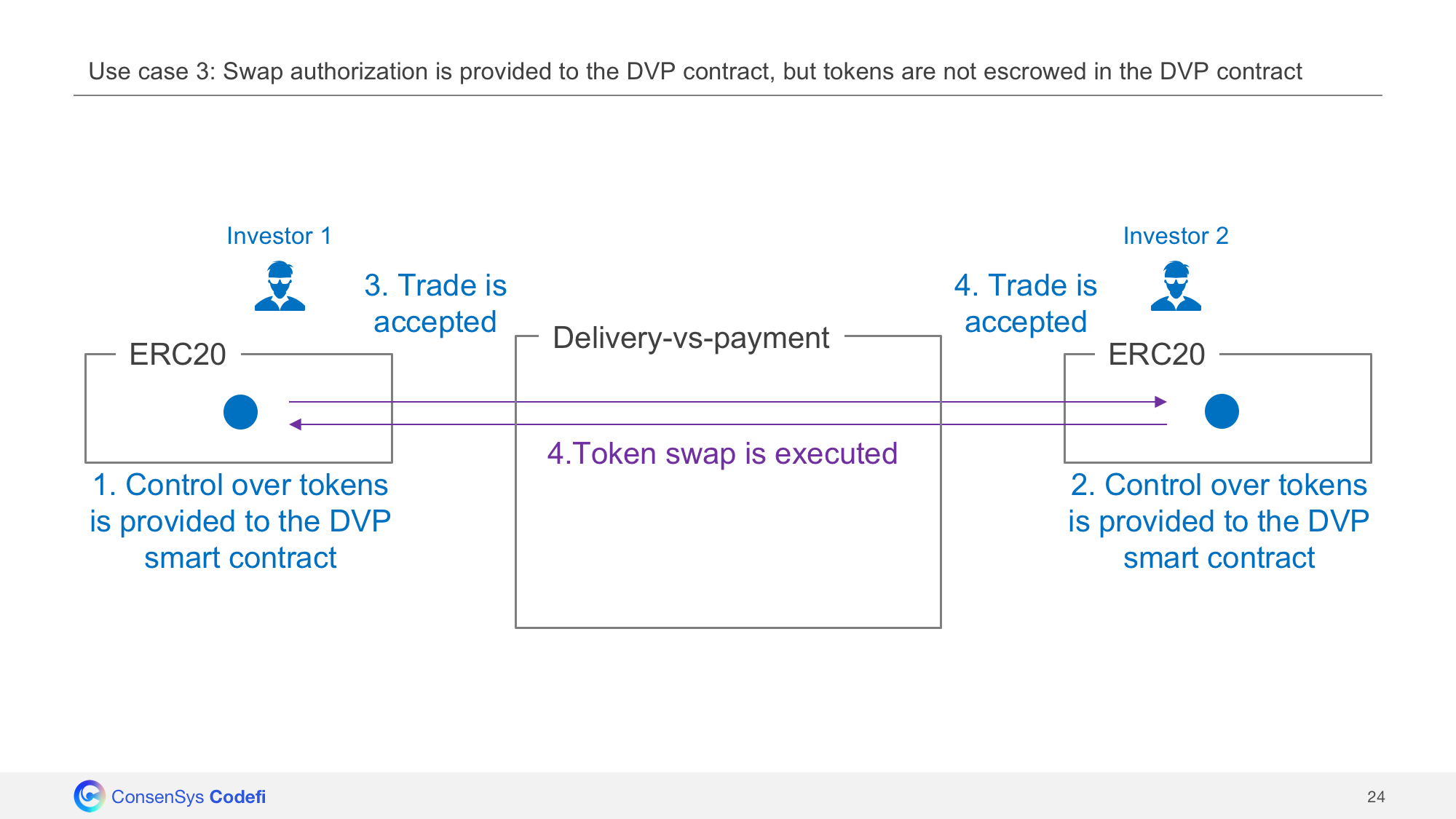
In case escrow mode is selected, tokens need to be escrowed in Swaps smart contract before the trade can occur. In case swap mode is selected, tokens are not escrowed in the Swaps. Instead, the Swaps contract is only allowed to transfer tokens ON BEHALF of their owners. When trade is executed, an atomic token swap occurs.
Expiration date
The trade can be cancelled by both parties in case expiration date is passed.
Claims
The executer has the ability to force or cancel the trade. In case of disagreement/missing payment, both parties can contact the “executer” of the trade to deposit a claim and solve the issue.
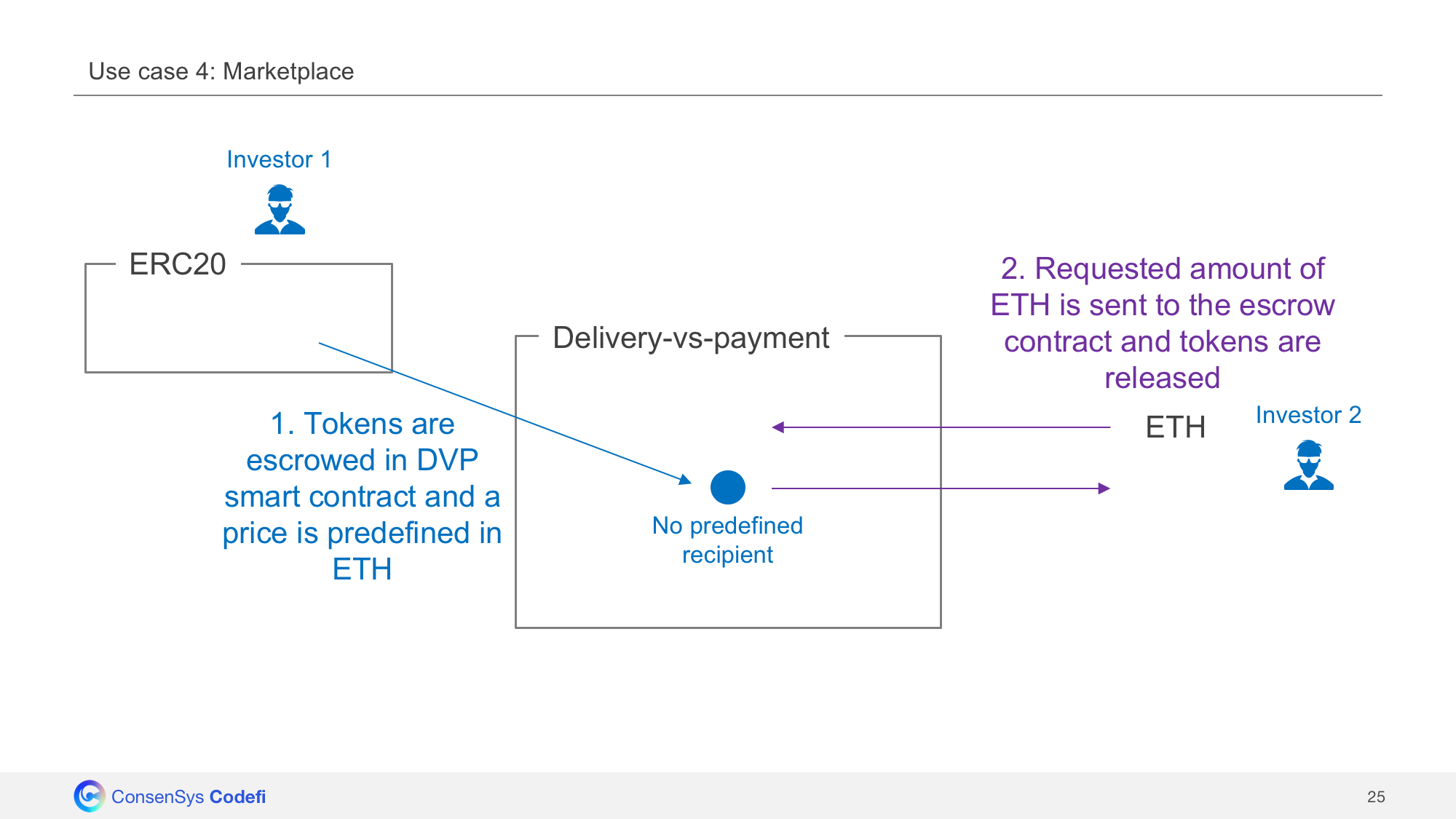
Marketplace
The contract can be used as a token marketplace. Indeed, when trades are created without specifying the recipient address, anyone can purchase them by sending the requested payment in exchange.
Price oracles
When price oracles are defined, those can define the price at which trades need to be executed. This feature is particularly useful for assets with NAV (net asset value).
Use case examples
The Swaps contract can be used for multiple use cases:
Use case 1: Tokens are escrowed in the Swaps contract while payment is made off-chain
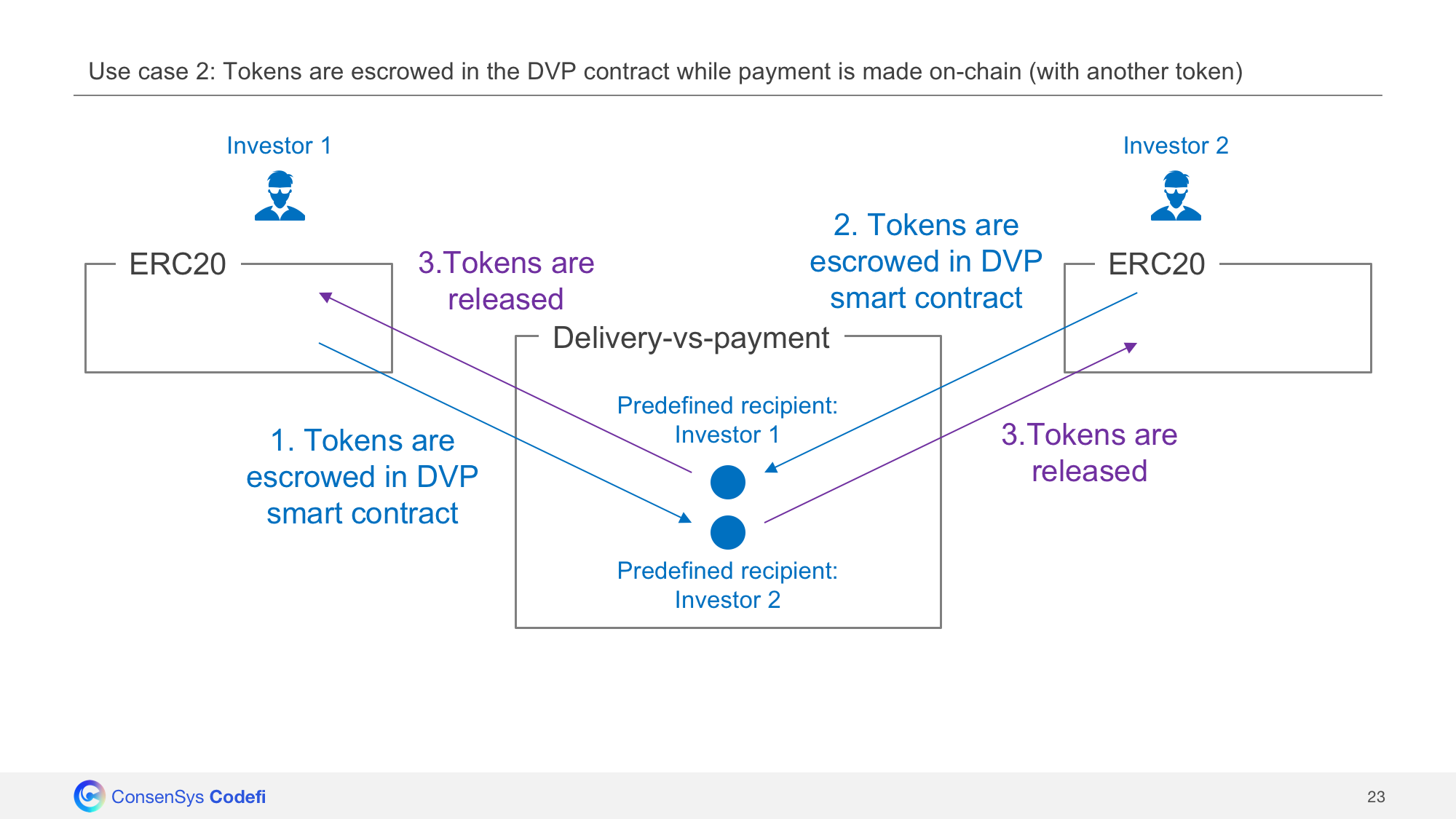
Use case 2: Tokens are escrowed in the Swaps contract while payment is made on-chain (with another token)
Use case 3: Swap authorization is provided to the Swaps contract, but tokens are not escrowed in the Swaps contract
Use case 4: Marketplace